Contents
- Foot Problems & the Elderly
- How Aging Affects Your Feet
- Balance and Gait Issues
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Hallux Rigidus (Big Toe Arthritis)
- Hammertoe
- Chronic Ankle Instability
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Gout
- Ankle, Hindfoot, and Midfoot Arthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease)
- FAQs on Foot Problems in the Elderly
- What are the foot problems in the elderly?
- What are age-related foot conditions?
- What is one of the most common disorders of the foot?
- What are some major foot problems?
- What are 8 common foot problems in the elderly?
- What is geriatric foot?
- Why do my feet hurt at 70 years old?
- How do you treat elderly feet?
- What is Foot Dysplasia?
- What is Acromesomelic Syndrome?
- What is Metadductus?
- What are the signs and symptoms of Fibrous Dysplasia?
- What is Williamson’s Syndrome?
- What is Schneider Syndrome?
- What is the Joubert Syndrome?
- What happens to your feet as you age?
- Why do old people need a podiatrist?
Foot Problems & the Elderly
Falls are a common and often deadly occurrence among our elderly population, accounting for thousands of fatal and nonfatal injuries every year. But while it’s true that getting older increases the risk of falling, it doesn’t have to be inevitable. With proper care and preventive measures, seniors can maximize their mobility and independence, reducing the likelihood of a fall.
Podiatrists are an important part of fall prevention for seniors. They are trained to identify those at risk for falls and are well-versed in treating foot and ankle conditions which may increase the chances of a person taking a tumble. Common problems that may lead to falls include:
- Osteoarthritis
- instability of the ankle or foot joints
- Dropfoot (Hemiplegia)
- posterior tibial tendonitis
- tendon contraction
- peripheral neuropathy
- flatfeet
- malformations in the toes
- Equinus Foot
- Charcot Foot
- gait abnormality
- lack of muscle coordination (Ataxia).
Of particular concern are issues such as:
- Chronic Ankle Instability
- Hallux Rigidus (big toe arthritis)
- Ankle, Hindfoot, and Midfoot arthritis
Unfortunately, falls are common occurrences among our elderly population, but they don’t have to be. By having regular check-ups with a podiatrist and taking preventive measures to reduce the danger of a fall, seniors can remain independent and safe.
How Aging Affects Your Feet
As people age, their feet can be subject to a variety of issues. Muscles can lose their density and sensation, resulting in reduced protection against the impact of walking. Veins can become more prone to pooling, which can cause swollen ankles and feet. The fat pads under the heel and ball of the foot may not necessarily thin out with age, however, the tissue composition may change so that it provides less cushioning.
Structural changes such as flatfoot and claw toes, due to muscle imbalances, are also common in older individuals. Bunions can form when bones in the big toe misalign, creating pressure points that can lead to discomfort. These age-related changes can contribute to foot soreness, experienced by up to 30% of older individuals. Fortunately, there are strategies you can use to look after your feet as you age.
Exercise can help maintain strength and flexibility in the foot muscles and tendons. Wearing supportive footwear with shock absorption is essential for reducing fatigue and strain. And simple steps such as regular moisturizing and soaking can keep feet healthy and comfortable. With the right care, you can get the most out of your feet at any age.
Balance and Gait Issues
As we age, our balance and gait can become increasingly compromised due to the effects of natural wear and tear on our bodies. In older adults, this can lead to a number of common foot problems, the most frequent being loss of balance and difficulty with walking. Balance issues manifest themselves in two main ways: impaired coordination when attempting to maintain upright posture, or instability when attempting to move or walk. Loss of balance can result in falls and mobility-related injuries, and weak or uneven gaits can cause pain and discomfort. Furthermore, these issues can be exacerbated if they lead to further complications such as tendonitis, joint stiffness, bursitis, and nerve damage.
Fortunately, balance and gait issues can be managed through proactive lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and getting adequate rest. The use of assistive devices such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs can also be beneficial in improving balance and gait. Physical therapists and other healthcare professionals can provide more specific advice and treatments tailored to individual needs. Ultimately, by making conscious efforts to manage balance and gait complications, older adults can remain independent and active for longer periods.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis is a common source of pain and discomfort experienced by many older adults. It occurs when the connective tissue that runs from the toes to the heel becomes inflamed, causing intense pain in the foot’s arch and heel. Those with this condition may feel shooting pains in the foot or heel every time they take a step, or find it difficult to stand for prolonged periods without experiencing pain.
To avoid or alleviate plantar fasciitis, there are several strategies one can employ. Anybody who suspects they have this condition should consult a medical professional. Additionally, it is important to stretch the calf muscles regularly, as tight calf muscles can contribute to plantar fasciitis. Shoes should also be comfortable and offer enough arch support and cushioning in order to reduce any additional stress on the feet. Anti-inflammatory medications can also provide temporary relief from pain associated with plantar fasciitis. Finally, investing in custom-made orthotics can improve the alignment of the feet and reduce pressure on the plantar fascia, providing long-term relief. With diligent care and attention, plantar fasciitis can be managed and prevented.
Hallux Rigidus (Big Toe Arthritis)
Hallux Rigidus is a degenerative joint disorder that affects the big toe, also known as the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. It usually develops in adults over the age of 30 and can lead to pain, swelling, stiffness, and range of motion issues. If left untreated, it can have a significant impact on day-to-day life with activities such as running, walking, or wearing high heels becoming uncomfortable.
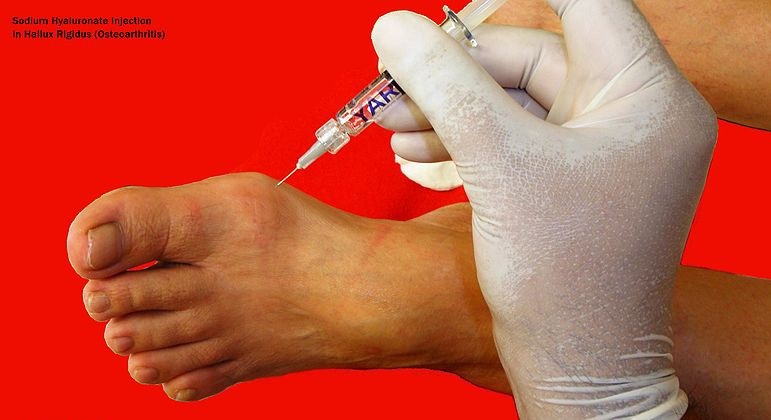
The key causes of this condition include biomechanics and structural abnormalities, such as excessive pronation or fallen arches. It can also be caused by an injury or work activities that require frequent stooping and squatting. Although not a genetic condition, some people may be more prone to Hallux Rigidus due to inherited foot types.
Diagnosing Hallux Rigidus requires X-rays to determine the extent of cartilage deterioration and bone spur formation. In addition, blood tests and aspiration can confirm septic arthritis.
Treatments include non-surgical methods like anti-inflammatory medications, cold therapy, choosing shoes with larger toe boxes and stiffer soles with a rocker panel feature, and wearing braces inside the shoe sole to limit toe bending. Cortisone injections may also help reduce inflammation. Surgery is only necessary if other treatments prove ineffective and depending on the severity of the condition, may involve a Cheilectomy for mild to moderate MTP damage, an Arthrodesis permanent fusion of bones if cartilage damage is severe, or an Arthroplasty ankle replacement with an artificial joint.
Hallux Rigidus is an unpleasant but manageable condition for those who are confident in identifying its early signs and who commit to following treatment regimens. With proper diagnosis and management, it is possible to maintain active lifestyles despite the presence of this disorder.
Hammertoe
Hammertoe is a common foot condition that occurs in adults over the age of 40. It is caused by an imbalance between the tendons, muscles, and ligaments that control the toes, leading to the formation of a hammer-like or claw-like shape. Patients with this condition may experience pain and discomfort in the affected toe, difficulty walking, and callusing on the top of the toe due to friction against shoes.
Treatment for hammertoe typically includes wearing proper-fitting shoes, orthotics, or splinting the affected toe. In more severe cases, surgery may be required to correct the deformity and restore full joint function. In addition, conservative measures such as physical therapy, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain and swelling.
It is important to seek treatment for hammertoe as soon as it is diagnosed in order to prevent any further complications from developing. With the right combination of therapies, individuals can manage their symptoms and prevent permanent damage to the toe. Additionally, those with the condition should take extra care to wear supportive shoes and protect their feet from pressure or injury.
Chronic Ankle Instability
Chronic Ankle Instability is a condition characterized by a recurrent weakening of the lateral (outer) side of the ankle. This can occur while walking, running, or even when standing still and is usually caused by a prior sprain, fracture, or other injury that did not completely heal. Common symptoms are pain, tenderness, and swelling.

Other causes may include arthritis, inflammation in the synovium (joint lining), a buildup of scar tissue, damage to a nerve, or nerve entrapment. Physiotherapy is a commonly used treatment to strengthen the ankle joint, often in conjunction with special bracing for support. Surgery may be required to tighten the ligaments on the outside of the ankle or graft a tendon from the other ankle if needed. With the correct diagnosis and treatment, Chronic Ankle Instability can be managed effectively.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy is a condition that affects many older adults and can lead to painful and uncomfortable symptoms. This disorder occurs when there is damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting sensations throughout the body. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include tingling in the hands and feet, numbness, burning, and weakness in the affected extremities. Individuals may also experience difficulty walking, as well as balance issues.
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition, but they generally involve physical therapy, skin care regimens, medications, nerve blocks, and dietary modifications. Peripheral neuropathy can be debilitating and cause considerable discomfort, so it is important to discuss any symptoms with your physician in order to find an effective treatment plan.
Gout
Gout is one of the most common foot problems among older adults, and it can cause considerable discomfort and mobility issues if left untreated. It is caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation, swelling, and significant pain. Common signs and symptoms of gout include intense joint pain, redness and warmth around the affected joint, and limited range of motion. Left unchecked, gout can lead to long-term damage and disability.
Fortunately, gout is highly treatable with medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. Medication such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Dietary changes are also important, as certain foods like red meat, seafood, and high-purine vegetables have been known to trigger gout attacks. Finally, limiting alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy weight can also be beneficial in managing gout symptoms.
It’s important for older adults to be aware of the risks associated with gout and take action to prevent or manage the condition. If you’re experiencing joint pain or mobility issues don’t hesitate to reach out for help – early diagnosis and treatment can make all the difference.
Ankle, Hindfoot, and Midfoot Arthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease)
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that affects the cartilage in various joints, including those of the ankle, hindfoot, and midfoot. There are three main types of arthritis: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. Each type has its own set of symptoms, which include swelling, stiffness and reduced mobility, tenderness and pain, and difficulty walking.
Non-surgical treatment for arthritis of the foot may involve cold therapy; anti-inflammatory and pain medications; using supportive footwear, custom orthotics, foot braces, balance braces, and casting; home therapy; participating in non-load bearing recreational activities; corticosteroid injections; and laser therapy. If non-surgical treatment does not provide enough relief or if pain persists, then surgery might be considered. Options may include arthroscopic debridement, arthrodesis (joint fusion), and arthroplasty (joint replacement).
Arthrodesis is most commonly used when the joint surfaces are severely damaged by the end stages of arthritis. It involves the complete fusion of the joint through the use of hardware to keep the bones in place while joint fusion occurs. Bone grafts may be necessary if there is bone loss present to ensure proper joint fusion. Fusion is usually successful, but additional surgery may be needed for bracing purposes if problems arise. Arthroplasty is another possible course of action in cases where severe pain limits patients’ ability to perform daily tasks and the ankle joint surfaces are completely destroyed. This procedure involves replacing the damaged joints with implants designed to match the patient’s anatomy and movement patterns to a long-lasting solution.
FAQs on Foot Problems in the Elderly
What are the foot problems in the elderly?
Common foot problems in older adults include plantar fasciitis, Morton’s neuroma, hammertoes, bunions, and diabetic neuropathy. Other age-related issues such as arthritis, osteoporosis, poor circulation, and a decrease in flexibility can all increase the chances of developing a more serious foot condition.
Age-related foot conditions often include flat feet, fallen arches, heel pain, calluses, corns, arch pain, ingrown toenails, and fungal infections. The weakening of the bones, muscles, and ligaments due to aging increases the risk of these types of disorders occurring.
What is one of the most common disorders of the foot?
Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common foot disorders seen in the elderly. It occurs when thick bands of tissue on the bottom of the foot become inflamed and cause sharp pain. The vast majority of cases are treated successfully with rest and conservative treatment options.
What are some major foot problems?
Major foot problems experienced by the elderly include flat feet, ankle sprains, gout, clubbed toes, hammertoes, carpal tunnel syndrome, hammertoe deformities, Achilles tendinitis, plantar warts, bunions, and diabetic neuropathy. While many of these disorders can be managed with lifestyle and/or therapeutic modifications, more severe cases may require medical attention or surgery.
What are 8 common foot problems in the elderly?
Eight common foot problems seen in older adults are flat feet, Morton’s neuroma, heel pain, hammertoes, bunions, diabetic neuropathy, plantar warts, and Achilles tendinitis. Since there are a variety of causes for each disorder, it is recommended to consult with your physician or podiatrist to identify the best treatment plan.
What is geriatric foot?
Geriatric Foot Care generally refers to the comprehensive care and management of an elderly patient’s feet. This includes assessing for any medical conditions that could affect their feet such as diabetes or vascular disease as well as any potential mobility issues that could arise due to structural changes. The goal of geriatric foot care is to reduce pain and discomfort while improving the quality of life for older patients.
Why do my feet hurt at 70 years old?
Many age-related issues can lead to chronic foot pain in older individuals. Common causes include arthritis, flat feet, bunions, hammertoes, gout, and other age-related disorders. Make sure to talk to your doctor about your symptoms so that you can get the proper evaluation and treatment.
How do you treat elderly feet?
Treating elderly feet involves comprehensive assessment and management of medical conditions that could affect the feet as well as addressing any mobility issues due to structural changes caused by aging. Treatment plans vary depending on the diagnosis but typically involve lifestyle modifications such as rest, physical therapy exercises, orthotics or shoes with specialized inserts, special creams or ointments, etc. In more severe cases surgery may be required.
What is Foot Dysplasia?
Foot dysplasia is a condition in which the bones in the foot do not form correctly during growth and development. This can lead to malformations of the toes, heel, and ankle that may be associated with pain or difficulty in walking. Treatment ranges from simple tools like orthotic devices to more complex surgical procedures.
What is Acromesomelic Syndrome?
Acromesomelic syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the shortening of the long bones in the arms and legs. It can also cause shortening of the ribs, fingers, and toes, as well as abnormalities in the facial features. The exact causes of this condition are unknown, but it is likely caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
What is Metadductus?
Metadductus is an abnormal positioning of the great toe where it appears to be pointing inward towards the other toes. It is usually seen in people who have tight calf muscles or high arches and can cause discomfort when walking or running. Treatment typically involves stretching exercises or custom orthotics to improve flexibility in the lower legs.
What are the signs and symptoms of Fibrous Dysplasia?
Fibrous dysplasia is a condition where the bone’s cells grow abnormally, resulting in excess fibrous tissue buildup. Symptoms vary depending on the affected area, but may include increased bone fragility, skeletal abnormalities, and swelling or pain at the site of the abnormal growth. Diagnostic imaging is necessary for confirmation of this condition.
What is Williamson’s Syndrome?
Williamson’s syndrome is a rare developmental disorder that mainly affects males. Its main characteristics include disproportionate short stature, mild mental retardation, deafness, heart abnormalities, and bent fingers. There is currently no specific treatment for this condition, although physical therapy may help improve mobility and muscle tone.
What is Schneider Syndrome?
Schneider syndrome is an inherited genetic disorder characterized by microcephaly (small head size) along with limb deformities such as webbed fingers and toe syndactyly (fused digits). In some cases, vision and hearing impairments may also be present. Treatment typically requires a multidisciplinary approach involving physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, dietary guidance, and other supportive therapies.
What is the Joubert Syndrome?
Joubert syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormal brain development that leads to problems with balance and coordination. Other signs and symptoms of this condition can include breathing difficulties, slow growth, kidney problems, and intellectual disabilities. Currently, there is no known cure for Joubert syndrome, but early diagnosis and management may help improve quality of life.
What happens to your feet as you age?
As we age, our feet tend to become less flexible and resilient due to wear and tear from years of use. This can lead to issues such as foot pain, poor balance, weakened muscles, decreased circulation, and joint stiffness. It’s important to maintain regular foot care to help reduce these age-related issues.
Why do old people need a podiatrist?
Older individuals often experience foot health issues due to reduced mobility caused by age-related conditions such as arthritis or diabetes. A podiatrist can help diagnose these conditions and provide tailored treatments that promote better foot health and comfort for their patients. Regular visits to a podiatrist can ensure that your feet remain healthy and functioning properly even as you age.
